
Building Materials
Civil engineering involves the use of various building materials such as concrete, steel, wood, and bricks to construct durable and safe structures like buildings, bridges, and roads.
View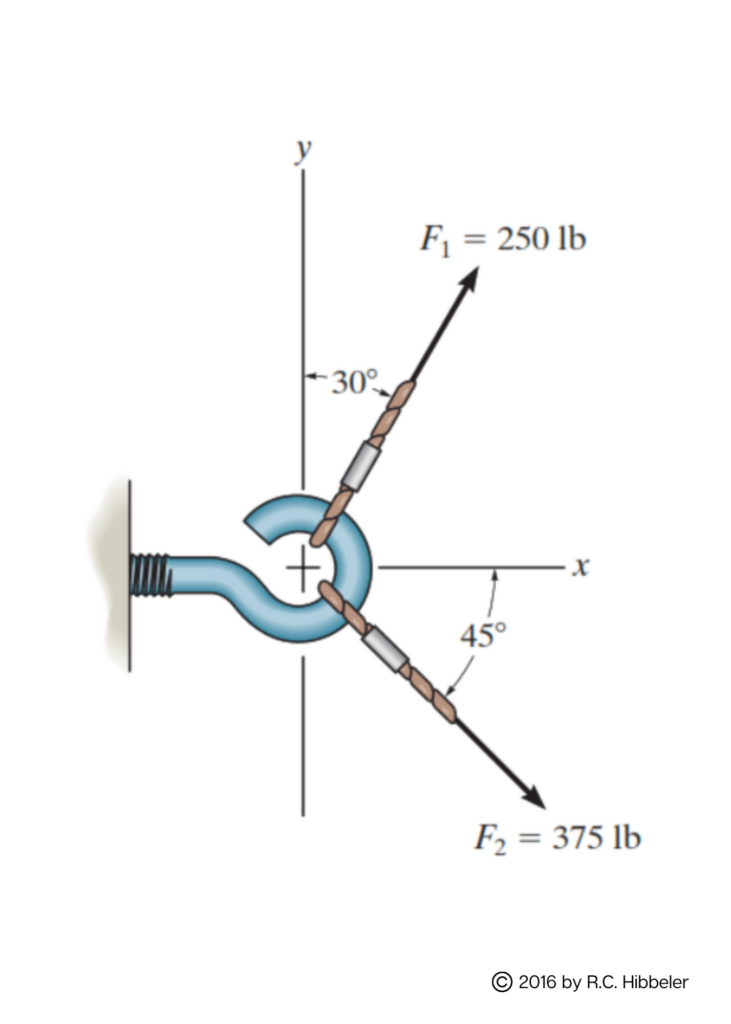
Engineering Mechanics
Engineering mechanics is a branch of civil engineering that applies principles of mechanics, physics, and mathematics to analyze and design structures and materials in the built environment.
View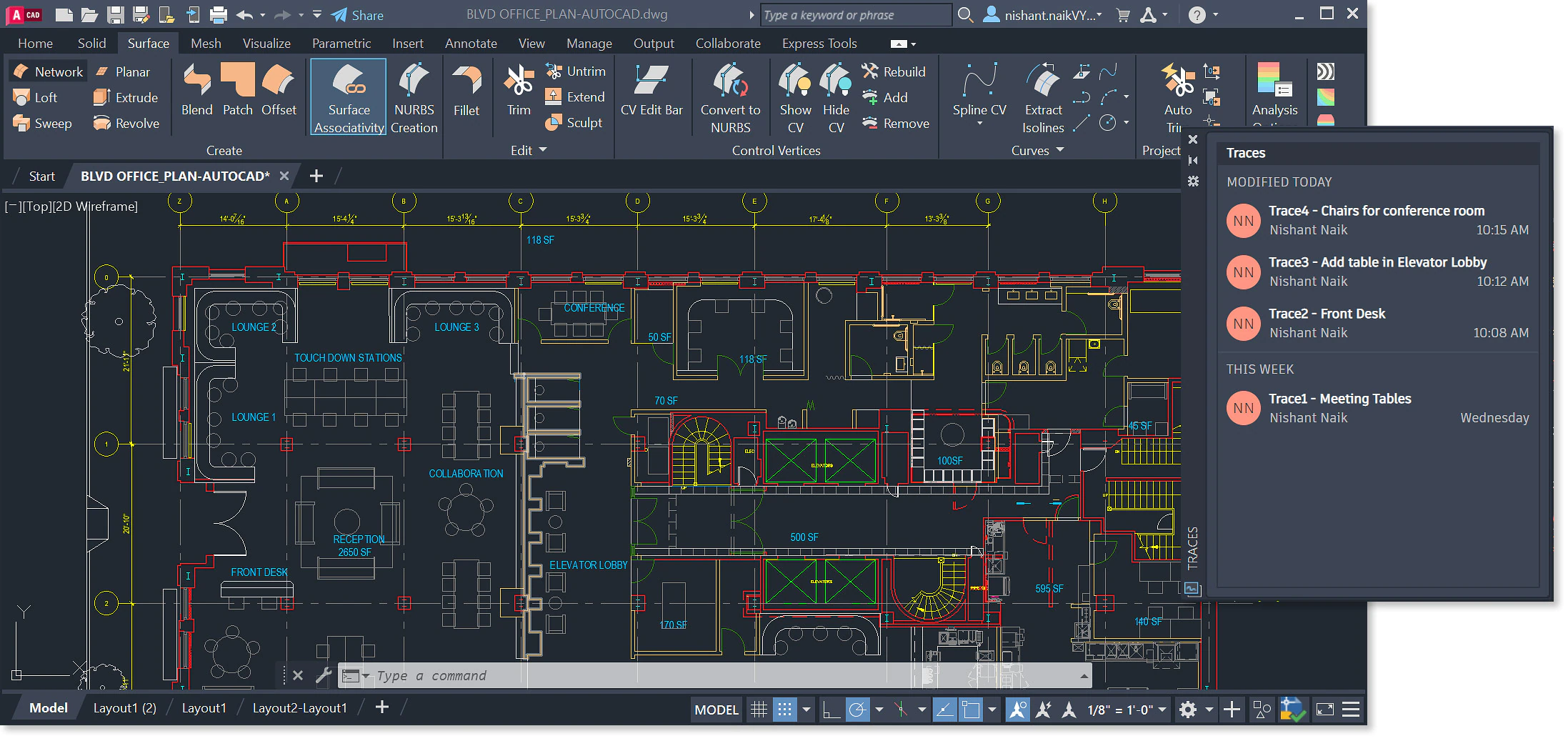
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a computer-aided design software used for creating 2D and 3D drawings. It is widely used in architecture, engineering, and construction industries for drafting and designing.
View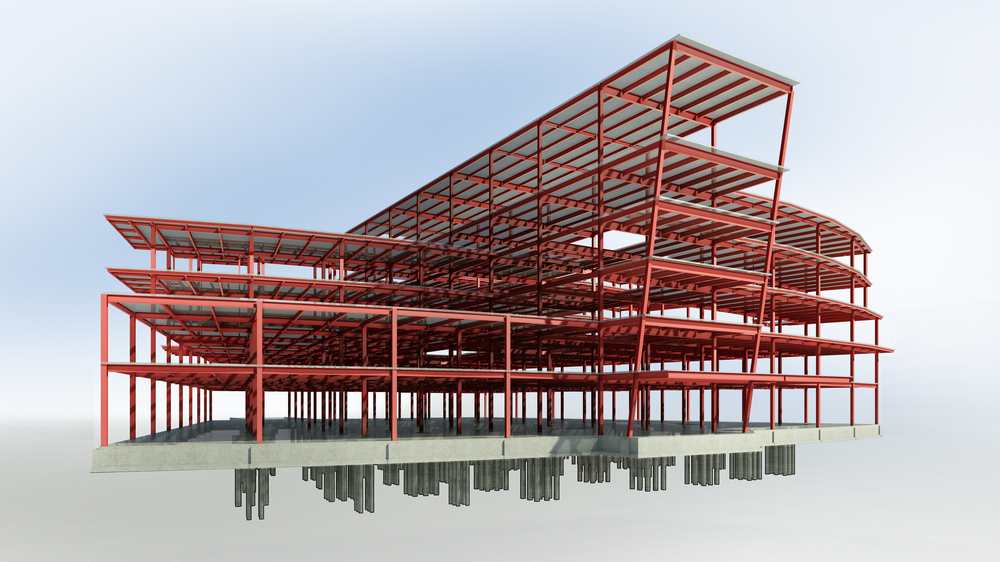
REVIT
Revit is a building information modeling software used for creating 3D models, floor plans, and construction documentation. It is widely used in architecture, engineering, and construction.
View
surveying
Surveying is the practice of measuring and mapping the earth's surface, often used in construction, engineering, and land development to ensure accuracy and safety.
View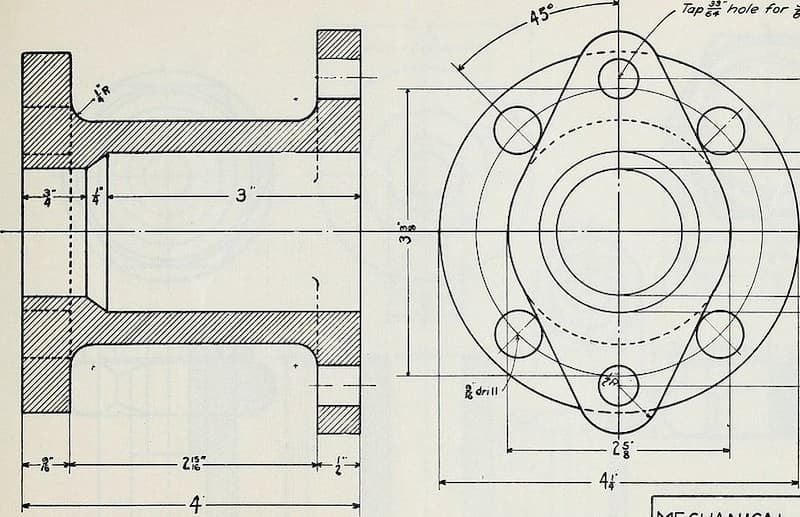
Engineering Drawing
Engineering drawing is a visual communication tool used to represent technical information such as dimensions, materials, and assembly instructions in manufacturing.
View
Fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the study of how fluids, such as liquids and gases, behave and interact with each other and with solid objects. It has applications in many fields, including engineering.
View
Aptitude
Aptitude refers to a person's natural ability or potential to acquire a particular skill or knowledge, but it is typically innate and can be measured through tests and assessments.
View
Engineering Mathematics
Engineering mathematics is a branch of mathematics that applies mathematical theories and methods to solve problems in engineering, science, and other related fields.
View
Concrete technology
Concrete technology refers to the science and technology involved in the production, processing, and use of concrete.It is widely applicable in the daily life and in construction practices.
View
Construction management
It involves planning and overseeing the construction process to ensure projects are completed on time, within budget, and to specifications.
View
Estimation and costing
Estimation and costing is the process of evaluating the cost of projects based on materials, labor, and other expenses.It typically involves evaluating in expenses to create a budget for the project.
View
Engineering Geology
Engineering geology involves the application of geology to civil engineering projects, including evaluating geological hazards, identifying suitable construction materials.
View
Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineering is a branch of civil engineering that deals with properties of soil, rock, and other geologic materials. It involves the analysis of slopes.
View
Environmental Engineering
Environmental engineering involves the application of science and engineering principles to protect and improve the environment, including air, water, and soil quality.
View
Hydraullic Engineering
Hydraulic engineering in civil engineering is concerned with the design and management of water resources and systems, including dams, canals, pipelines, drainage systems.
View
Hydrology
Hydrology in civil engineering involves the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water in the natural environment, including its interaction with soil and vegetation.
View
Irrigation
Irrigation is the process of artificially supplying water to crops or landscapes to sustain their growth and health. It involves the design, construction, and management of water.
View
Transportation Engineering
Transportation involves the planning, design, construction, and management of infrastructure systems such as highways, airports, railways, and transit systems to ensure safe.
View
Prestressed concrete
Prestressed concrete is a construction material that has been pre-compressed to increase its tensile strength and reduce the risk of cracking or structural failure.
View